【C++】
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
long long n,a[1010],m;
void print(stack<int> Temp)
{
if(Temp.empty()) return;
int T=______(1)______;
Temp.pop();
print(Temp);
printf("%d ",T);
}
void exchange()
{
stack<int> arr;
int i=0,num=0;
while (______(2)_______)
{
while(m>0 && i<n)
{
if(m>=a[i])
{
arr.push(i);
______(3)_______;
}
i+=1;
if(m==0)
{
stack<int> arrT=arr;
print(arrT);
printf("\n");
num+=1;
}
}
if(______(4)_______)
{
i=arr.top();
arr.pop();
m+=a[i];
_____(5)______;
}
}
if(num==0)
puts("No");
else
printf("%d\n",num);
}
int main()
{
cin>>m>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) cin>>a[i];
exchange();
return 0;
}
【Python】
def exchange(t,pricelist):
n=len(pricelist)
stack=[]
i=0
num=0
while _____(1)_______:
while t>0 and i<n:
if t>=int(pricelist[i]):
stack.append(i)
______(2)________
i+=1
if t==0:
print(stack)
num+=1
if _____(3)________:
i=stack.pop()
t+=int(pricelist[i])
______(4)_______
if num==0:
print('No')
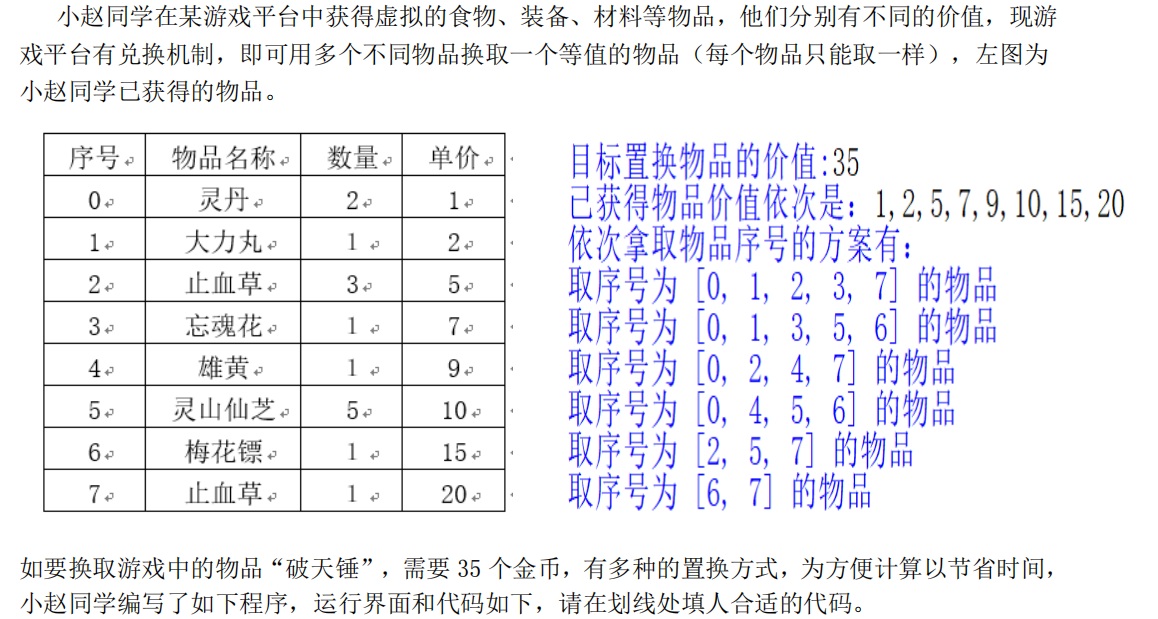
m=int(input()) #目标置换物品的价值
price=input() #已获得物品价值依次是
p=price.split(',') #将输入的内容以','作分隔,并转换为列表
exchange(m,p)